Burger (pronounced bur-ger or bur-gha)
(1) A clipping of hamburger.
(2) A disc-shaped food patty (or patty on a bun), sometimes
containing ingredients other than beef including vegetarian concoctions.
(3) In Pakistani slang (usually derogatory), as burger or
hamburger, a stereotypically well-off Pakistani aspiring to a westernized
lifestyle.
(4) In Internet slang (apparently beginning on 4chan), an
American (as in a white, US citizen); of or relating to Americans.
(5) In computer graphical user interfaces (GUIs), as hamburger
button, an icon with three horizontal lines (the resemblance being to the
stacked ingredients of a burger). The
hamburger label was applied retrospectively, the original idea being to
represent a list, the icon’s purpose being to open up a list of options; it’s
thus also known as the “collapsed menu icon”.
1939: An invention of US English, extracted from hamburger
by misunderstanding (ham + burger). Use
of the noun hamburger is not exclusive to fast food. As early as 1616 it was noted as being the
standard description both of someone “a native of the city of Hamburg" and
also of ships “registered with Hamburg as their home port"). From 1838 it was the name of a black grape
indigenous to Tyrolia and after 1857, a variety of hen. Technically the meat product is a specific
variation of shaped, ground beef (minced meat); as a meatball is a sphere and
meatloaf is a rectangular cuboid, hamburgers (and burgers) are discs. Burger, burgeria & burgery are nouns; the noun plural is burgers.
Not that the burger is even exclusively fast food. Some very expensive burgers have been created
although, compared to their availability, there’s considerably less publicity about
their sales. As pieces of conspicuous
consumption they must have a niche but Netherlands diner De Daltons‘ (Hoofdstraat
151, 3781AD, Voorthuizen) opted to couple indulgence with a good cause, the
proceeds of their Golden Boy burger donated
to the local food bank. Emphasizing
quality rather than sheer bulk, the Golden
Boy was actually a good deal less hefty than some of the huge constructions
burger chains in the US have offered to satisfy the gulosity of some (burgers
with names like Heart Attack, XXXL, 55 oz
Challenge, One Pound of Elk, Sky-high Scrum, Monster Thickburger & Killer hardly subtle hints at the target
market).
By comparison, the price tag of €5,000 (US$5,100)
aside, the Golden Boy seems almost
restrained, though hardly modest, presented on a platter of whiskey-infused
smoke, its ingredients including Wagyu beef, king crab, beluga caviar, vintage
Iberico Jamon, smoked duck egg mayo, white truffle, Kopi Luwak coffee BBQ
sauce, pickled tiger tomato in Japanese matcha tea, all assembled on two Dom
Perignon infused gold-coated buns. The
chef insists it still just a burger and should be eaten using the hands, a nice
touch being that because the buns are covered in gold leaf, fingers will be
golden-tinted when the meal is finished.
A Golden Boy must be ordered two weeks in advance and a deposit of €750 (US$765)
is required.
People around the world had no doubt for centuries been
creating meatloaves, meatballs and meat patties before they gained the names
associated with them in Western cuisine.
The idea is simply to grind-up leftover or otherwise unusable cuts, add diced
vegetables & spices to taste and then blend with a thickening agent (flour,
breadcrumbs, eggs etc) to permit the mix to be rendered into whatever shape
is desired. The hamburger is no more an
invention of American commerce that the sandwich was of the English aristocracy.
The words however certainly
belong to late-stage capitalism. Hamburger
is noted in the US as describing meat patties in the late nineteenth century
(initially as hamburg steak), the connection apparently associative with German
immigrants for whom the port of embarkation was often Hamburg although there is
also a documented reference from 1809 in Iceland which referred to “meat smoked
in the chimney” as Hamburg beef. There are a dozen or more stories which
speculate on the origin of the modern hamburger but, in the nature of such an
ephemeral craft, there is little extant evidence of the early product and there’s
no reason not to assume something so obvious wasn’t “invented” in many places
at much the same time. The earliest
known references which track the progression seem to be hamburger sandwich
(1902), hamburger (1909) & burger (1939) although burger was by then an element
in its own right, acting as a suffix for the cheeseburger (1938). The culinary variations are legion: baconburger;
cheeseburger; fishburger; beefburger; bacon & egg burger; whale burger, dog
burger & dolphin burger (those three still a thing in parts of the Far East
although not now widely publicized); vege burger; vegan burger; kangaroo
burger, camel burger & crocodile burger (the Australians have a surplus of
all these fine forms of animal protein), lamb burger, steakburger, soyburger,
porkburger etc. Opportunistic constructions like burgerlicious are created as required. The homophones are Berger
& burgher (in English use a middle-class or bourgeois person). The noun plural is burgers.
Blogger Dario D had noticed that visually, the Big Macs he bought from random McDonalds outlets didn’t quite live up to the advertising. That’s probably true of much industrially produced food but what was intriguing was what was revealed when he applied a tape measure to his research. It seems Big Macs can’t be made exactly like they look in the advertising because then they would be too big to fit in the packaging.
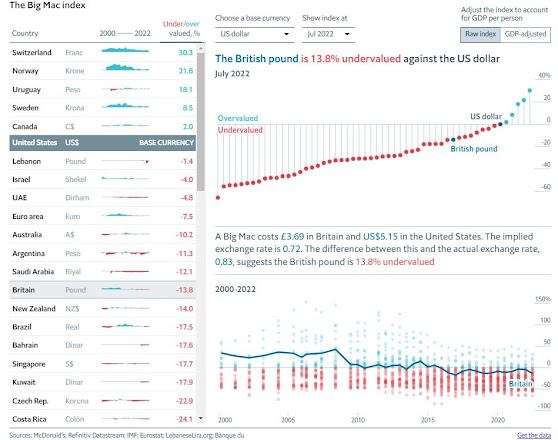
The Big Mac Index (BMI) was created by The Economist newspaper in 1986 and that the abbreviation is the same as for "body mass index" is presumed coincidental although the publication's caption writers often display some linguistic flair so who knows? The currency-related BMI is a price index which provides an indicative measure of purchasing power parity (PPP) between currencies and uses movements in the burger's price to suggest whether an official exchange rate is over or under-valued. The newspaper has never claimed the BMI is an authoritative economic tool and has always documented its limitations but many economists have found it interesting, not so much the result on any given day but as a trend which can be charted against other metrics. It was an imaginative approach, taking a single, almost standardized commodity available in dozens of countries and indexing the price, something which should in each place be most influenced by local factors including input costs (ingredients & labour), regulatory compliance, corruption and marketing. Even those who don’t agree it has much utility as an economic tool agree it’s fun and other have published variations on the theme, using either a product made in one place and shipped afar or one made with locally assembled, imported components.
The BMI also brought to wider attention the odd quirk. Although its place in the lineup has been replaced by a chicken-based dish, the Big Mac used to be on the McDonald's menu in India although, in deference to Hindu sensitivities (and in some states actual proscription), it was made not with beef but with lamb; it's said to taste exactly the same which seems a reasonable achievement. Burgers can be thematic and these are based on the seven wonders of the ancient world:
The Colossus of Rhodes (that’s a big burger with Greek
lamb)
The Great Pyramid of Giza (has an Egyptian sauce)
The Hanging Gardens of Babylon (vegetarian (lettuce
hanging out of it))
The Lighthouse of Alexandria (a lighter (low calorie) burger)
The Mausoleum at Halicarnassus (a traditional, very high calorie
burger)
The Statue of Zeus at Olympia (has a very hot
sauce)
The Temple of Artemis (Diana) at Ephesus (made with square or
rectangular bun and finished with burnt edges)
Lindsay Lohan with burger.