Waterfall (pronounced waw-ter-fawl or wot-er-fawl)
(1) A steep fall or flow of water in a watercourse from a
height, as over a precipice; a cascade of falling water where there is a
vertical or almost vertical step in a river.
(2) A hair-style using long, loose “waves”.
(3) As “waterfall development”, “waterfall management”
and “the waterfall model”, descriptions of product research & development
(R&D) (especially in tech) including sequential stages, from conception and
design through testing and implementation, hopefully to result in a final delivered
product.
(4) Figuratively, any waterfall-like outpouring of
liquid, smoke etc.
(5) In slang (originally US but now widespread), the
action of drinking from a vessel without touching it with the lips (a sanitary precaution
with shared vessels).
(5) In the smoking of weed, a particular design of bong.
Pre 1000: From the Middle English waterfal & waterfalle,
from the Old English wæterġefeall (waterfall)
and cognate with the Old Norse vatnfall,
the West Frisian wetterfal
(waterfall), the Dutch waterval (waterfall),
the German Wasserfall (waterfall) and the Swedish vattenfall (waterfall). The colloquial
use to describe (1) a necktie, (2) a cravat, (3) a chignon (in hair-styling, a
low bun or knot positioned at or close to the nape of the neck) or (4) a beard
are now effectively extinct. Waterfall’s
synonyms in general use (though hydrologists are more precise) include cascade,
cataract, sault (old Canadian slang more often used of river rapids) and the
clipping falls. Waterfall is a noun verb
& adjective and waterfalling & waterfalled are verbs; the noun plural
is waterfalls.
The construct was water + fall and the Modern English
spelling appears to have been a re-formation from around the turn of the
sixteenth century. The noun “water” was
from the Old English wæter (water),
from the Proto-West Germanic watar,
from the Proto-Germanic watōr (water),
from the primitive Indo-European wódr̥ (water). The verb “water” was from the Middle English wateren,
from the Old English wæterian, from the
Proto-Germanic watrōną & watrijaną, from the Proto-Germanic watōr (water), from the primitive Indo-European
wódr̥ (water). The noun “fall” was from the
Middle English fal, fall & falle, from the Old English feall & ġefeall (a falling, fall) and the Old English fealle (trap, snare), from the Proto-Germanic fallą & fallaz (a
fall, trap). It was cognate with the Dutch
val, the German Fall (fall) & Falle (trap,
snare), the Danish fald, the Swedish fall and the Icelandic fall.
The verb “fall” was from the Middle English fallen, from the Old English feallan
(to fall, fail, decay, die, attack), from the Proto-West Germanic fallan (to fall), from the Proto-Germanic
fallaną (to fall). It was cognate with the West Frisian falle (to fall), the Low German fallen (to fall), the Dutch vallen (to fall), the German fallen (to fall), the Danish falde (to fall), the Norwegian Bokmål falle (to fall), the Norwegian Nynorsk falla (to fall), the Icelandic falla (to fall), the Albanian fal (forgive, pray, salute, greet) and
the Lithuanian pùlti (to attack, rush).
Two views of Niagara Falls: Between June-November 1969 (left), a temporary dam was built to stem the usual flow so geological studies could be conducted to ascertain the condition of the rocks and assess the extent of erosion. After rectification work was carried out, the temporary structure was dynamited, an event promoted as a tourist attraction. In 1885 (right), the falls underwent one of its occasional freezes. Usually, these are what hydrologists call "partial freezes" (of late there have been a few: 2014, 2017 & 2019), the only (almost) "total freeze" recorded in 1848 although that was induced by the accumulation of ice on Lake Erie which caused a "natural dam" to form, stopping the flow of water to the Niagara River. It was this rather than a "total freeze" of the falls which caused the phenomenon.
Lindsay Lohan with waterfall, Guanacaste Gold Coast, Costa Rica, January 2016.
For most of us, we know a waterfall when we see one: it’s a point in a waterway (usually a river) where the water falls over a steep drop that is close to literally vertical. However, among hydrologists, there’s no agreed definition about the margins such as when something ceases to rapids and becomes a waterfall, some insisting that what lay-people casually call “waterfalls” are really “cataracts” or “cascades”. To most of us there to admire the view, it’s a tiresome technical squabble among specialists but among themselves they seem happy for the debate to continue and some have even suggested precise metrics which can be mapped onto any formation.
Wasserfall (Waterfall), the embryonic SAM
Wasserfall (project Waterfall) was an early
SAM (surface to air missile) developed by the Nazi armaments industry. Although never used, it was highly
influential in the post-war years. In
his memoirs (Inside the Third Reich
(1969)), Albert Speer (1905–1981; Nazi court architect 1934-1942; Nazi minister
of armaments and war production 1942-1945) discussed both the weapons systems with
which he as minister was usually in some way connected and the political
in-fighting and inter-service rivalries which hampered their development. Although his writings are not wholly reliable
(there was much he choose not to say on his contribution to anti-Jewish
measures and his knowledge of the holocaust), on industrial and technical
matters historians regard his account as substantially accurate (if incomplete). Interestingly, after reading in Spandau prison
a smuggled copy of the memoir (Ten Years
and Twenty Days (1958)) of Karl Dönitz (1891–1980; as Grand Admiral head of
the German Navy 1943-1945, German head of state 1945) who had been a fellow
prisoner for the first decade of Speer’s twenty-year sentence, without any
sense of irony, he remarked in his (extensively edited) prison journal (Spandau: The Secret Diaries (1975)):
“Where
he discusses military operations and the questions of armaments, the book is interesting
and probably also reliable. His political
attitude, on the other hand, his relationship to Hitler, his childish faith in
National Socialism – all that he either wraps in silence or spins a veil of
sailor’s yarns. This is the book of a
man without insight.”
Speer re-invented himself by
wrapping in veils of silence anything too unpleasant to admit and spun plenty
of veils so appealing that for decades there were many who, for various
reasons, draped them over his past. He
wasn’t a man without insight but compared with Dönitz, he had much more guilt
to conceal and thus more need of selective silence & spin.
Speer regarded the regime’s failure
to devote the necessary resources to the Wasserfall project as one of Adolf Hitler's (1889-1945; Führer (leader) and German head of government 1933-1945 & head of state 1934-1945) many strategic blunders which, by 1943, had made defeat inevitable. Having delayed development of the
revolutionary Messerschmitt Me 262 jet fighter (deployed at scale mass it would
have been a devastating weapon against the Allied bomber fleets then laying
waste to German cities and industry), Hitler took the decision to afford the
highest priority to the A4 (better known as the V2) rocket to retaliate against
English cities; psychologically, Hitler always wanted to be on the offensive and
would later appal the experts by demanding the Me 262 be re-designed as a fast,
light bomber. As a delivery system the
V2 was a decade ahead of its time and there was then no defense against the
thing but it was a hugely expensive and resource-intensive way to deliver an
explosive load under a tonne. As Speer
noted, even if it became possible to produce and fire the projected 900 a
month, that would mean a daily bomb-load of some 24 tonnes falling on England
and that at a time when the Allied bomber groups were on average dropping some 3000
tonnes a day on German targets. Hitler
wasn’t wrong in predicting the use of the V2 against civilian targets would
have an effect well beyond the measure of the tonnage delivered and the
historians who claimed the disruption to the allied war effort caused by the V1
(an early cruise missile) & V2 was “negligible” were simply wrong but to
have been an effective strategic weapon, at least hundreds of V2s a day would need to have found their targets.
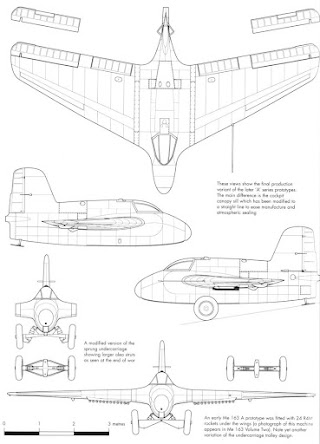
Captured blueprints and photographs from the Wasserfall project's development.
Speer admitted he “…not only went along with this decision on
Hitler's part but also supported it. That was probably one of my most serious
mistakes. We would have done much better
to focus our efforts on manufacturing a ground-to-air defensive rocket. It had already been developed in 1942, under
the code name Wasserfall (Waterfall), to such a point that mass production would
soon have been possible, had we utilized the talents of those technicians and scientists busy with [the V2] under Wernher von Braun (1912–1977).”
He added that von Braun’s team was
employed to develop weapons “…for the
army, whereas air defense was a matter for the air force. Given the conflict of interests and the fierce
ambitions of the army and the air force, the army would never have allowed its
rival to take over the installations it had built up…” The difference in resource allocation was
stark, more than ten times the number of technical staff working on the V2
compared to Waterfall and other anti-aircraft rocket projects (such as the small
Taifun (Typhoon)). The attraction of the anti-aircraft rockets was
obvious as Speer noted: “Waterfall was capable
of carrying approximately six hundred and sixty pounds of explosives along a directional beam up to
an altitude of fifty thousand feet and hit enemy bombers with great accuracy. It was not affected by day or night, by
clouds, cold, or fog. Since we were later able to turn out nine hundred of the
offensive big rockets monthly, we could surely have produced several thousand of these smaller and less
expensive rockets per month. To this day I think that this
rocket, in conjunction with the jet fighters, would have beaten back the Western
Allies' air offensive against our industry from the spring of 1944 on. Instead, gigantic effort and expense went into
developing and manufacturing long-range rockets which proved to be, when they
were at last ready for use in the autumn of 1944, an almost total failure [a comment which, combined with
Allied propaganda and disinformation, influenced for decades many post-war
historians]. Our most expensive project was also our most foolish one. Those
rockets, which were our pride and for a time my favorite armaments project,
proved to be nothing but a mistaken investment. On top of that, they were one
of the reasons we lost the defensive war in the air.”
Whether a mass-produced Waterfall would have been an effective weapon against the mass-bomber formations has divided analysts. While the technology to produce a reliable directional mechanism had been mastered, what Germany never possessed was a proximity fuse which would have enabled the explosive charge to be triggered when a bomber was within range; instead the devices relied on impact or pre-set detonators. Presumably, had other projects been suspended and the resources re-directed to Waterfall, mass production may have been possible and even if only partially successful, to disrupt a bombing offensive it was necessary only to inflict an ongoing 5-10% loss rate to make the campaign unsustainable. Given the inevitable counter-measures, even that would likely have proved challenging but economic reality meant Waterfall probably did offer a more attractive path than the spectacular V2 and given the success in related fields, it was not impossible that had priority been granted, proximity fuses and other technical improvements may rapidly have appeared. As it was, Waterfall (like Typhoon, Me 262, V2 and an extraordinary range of other intriguing projects) was the subject of a post-war race between the Russians, the Americans and the British, all anxious to gather up the plans, prototypes, and personnel of what were clearly the next generation of weapons. As a proof of concept exercise Waterfall was convincing and within years SAMs were a vital component of defensive systems in most militaries.
The waterfall motif: Grill on the 1975 Imperial LeBaron Crown Coupe (left) and the Liebian International Building in China (right).
In design, "waterfall" can be a motif such as used for the grill on the 1975 Imperial LeBaron Crown Coupe. It can also be literal and architects have many times integrated water-flows as an external design element but at 108 metres (354 feet) high, the one on the façade of the Liebian International Building in south-west China is easily the world’s tallest. An eye-catching sight, the waterfall isn't run all that often (which must disappoint influencers who turn up with cameras ready) because it’s said to cost some 900 yuan (US$125) per hour just to pump the water to the top and, with the downturn in the property market, the building's revenues have fallen short of expectation. When completed and displayed in 2016, the waterfall attracted some criticism on environmental grounds, water shortages far from unknown in China although the builders (Ludi Industry Group) pointed out the signature feature uses storm-water runoff, rainwater and groundwater, all stored in vast underground tanks. It may for a while be the last example of exuberance to show up among China's skyscrapers, Xi Jinping (b 1953; general secretary of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and paramount leader of the People's Republic of China (PRC) since 2013) in 2014 calling for an end to what he called "weird architecture". Mr Xi thinks buildings should be "suitable, economic, green and pleasing to the eye" rather than "oversized, xenocentric & weird". Those skilled at reading between the CCP's lines decided the president had called the architects "formalists". They would have taken note.
On TikTok, a small but active community of those who find waterfalls mesmerizing post video clips.