Periscope (pronounced per-uh-skohp)
(1) Any of a number of optical instruments used to view
objects that are above the level of direct sight or in an otherwise obstructed
field of vision, consisting essentially of a tube with an arrangement of prisms
or mirrors and, usually, lenses; used especially in submarines and military
reconnaissance.
(2) A periscopic lens.
(3) A now defunct live video streaming app for Android
and iOS, acquired by Twitter (before launch) in 2015 and depreciated between 2016-2021.
(4) A general or comprehensive view (obsolete).
1815–1825: The construct was peri + scope, a back
formation from periscopic from the Ancient Greek periskopein (to look around).
Peri- was from the Ancient
Greek περί (perí) (about, around) and
was cognate with the primitive Indo-European via. Scope was from the From
Italian scopo (purpose), from the Latin
scopus (target), from the Ancient Greek
σκοπέω (skopéō) & σκοπός (skopós) (examine, inspect, look to or
into, consider), from σκέπτομαι (sképtomai),
from the primitive Indo-European speḱ- and etymologically related
to both skeptic and spectrum. Periscope is
a noun (and a largely archaic verb), periscopic is an adjective and periscopically
an adverb. The present participle is periscoping
and the past participle periscoped); the noun plural is periscopes.
Although variations of the device had existed for
decades, the word periscope either wasn’t used or was at least not in general
use before 1899 but as early as 1865 it attested as a technical term in
photography. The concept of the
periscope (then called the polemoscope)
and using two angled lens had been described as early a 1647 in a work
discussing the geological nature of the moon although then it was envisaged as
device suitable for military observation. Undocumented and undated sketches thought to
date from decades earlier have also been unearthed but, although conceptually
accurate, their exact purpose is unclear and they may have been architectural
drawings.
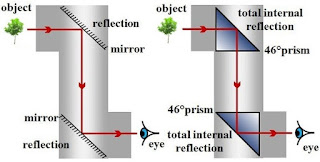
The first naval
periscopes appeared in 1854, constructed by placing two mirrors in a vertical
tube, fixed at each end at a 45° angle and were a noted feature of the early
submarines used in the US Civil War (1861-1865); by the dawn of the twentieth
century they’d begun regularly to be part of the design although the great
innovation was the retractable periscope in 1902, then known as the skalomniscope or omniscope. The retractable
periscope quickly became a standard fitting to submarines and proved an
important factor in the success they enjoyed during the First World War.
Surprisingly, given how simple the adaptation would have
been, periscopes were little-used by nineteenth century armies but proved to be
an invaluable addition to the kit in the trench warfare of 1914-1918,
providing a wide vista for observation without exposing the viewer to the risk
of attracting sniper fire. One invention
which proved of less utility was the so-called periscope-rifle, a kind of remote-controlled
infantry rifle mounted atop the trench parapet, aimed and fired by a soldier in
a safe position below. Success was
limited. More useful were devices called
stereoscopic rangefinders, periscopic binoculars with grids which enabled
trained observers to estimate the distance to a target.
The Lamborghini Countach "Periscopio"
When shown at the 1961 Geneva Motor Show, the Jaguar E-Type (XKE) created a sensation. At the same event, ten years later, the Lamborghini Countach LP500 created almost as much excitement and its lines have been the template for most Lamborghinis since. In a sense, progress in the design of such machines paused at that point, everything since (and not just by Lamborghini) a refinement of the yellow wedge. Although it was a small and functionally unsatisfactory aspect of the dramatic LP500, it was the abortive periscopio (periscope) which would be used to characterize the first 157 (some sources insist 158) LP400 production cars, the periscopio rear view concept lending the roof its distinct shape. The factory’s documents don’t reveal whether the idea of the periscope was the inspiration of an individual or emerged from a committee but the thought was that in such a low-slung vehicle, the driver would be afforded a better view from a lens mounted atop the roof than would be provided by a conventional rear-view mirror aligned with the rear-window. Donnelly Corporation in the US delivered a working version of the periscope mirror system, a number of which had actually be built in the era for use in the ESV (Experimental Safety Vehicle) projects which a number of manufacturers had developed to test their implementation of the engineering which would be required to conform with the safety regulations soon to come into force.
1974 Lamborghini Countach LP400 roof detail.
However,
during testing, it became obvious it was not a desirable solution, the positioning
dictated by the then unique profile requiring the driver too often to avert
their eyes from what was ahead adequately to focus on what lay behind. Nor did the designers warm to the small bulge
which would have to be added to the roofline to accommodate the hardware; aesthetics
meant little to those who penned ESVs but they were prized by Italian stylists
and consequently the periscope was abandoned.
However, whether for reasons of economy or constraints of time, although
the bulge was deleted, the remaining periscopio
roof shape was retained and in 1974 entered production as part of the LP400 although it
now provided no obvious functional advantage except making the cabin a little
brighter and perhaps adding some rigidity to the structure although there may
have been some aerodynamic cost, the interruption to what would otherwise be a
smooth surface presumably generating additional drag. Whatever the drawbacks however, stylistically,
it’s always been admired.
1977 Lamborghini Countach LP400.
Those first 157 LP400s
were also the closest the production cars would be to the original, unadorned wedge
which had made such an impact when displayed at the 1971 Geneva Motor Show as
the Lamborghini LP500 concept. That it
was described as a concept was important because the LP500, although
fully-functional, was no prototipo (prototype),
and the uncompromising original could not without modification be
transformed into a practical production car, hence the many scoops to ensure
adequate cooling as well as the deletion of the periscope, changes to the
construction method used for the frame, a reduced-capacity engine, the
substitution of analogue instruments for the space-age electronica and some
enlargement of the platform to make the thing more habitable. Still, the LP400 was remarkably close to the
startling original and tellingly, of all two-thousand odd which would in five
generations be produced between 1974-1990, it would be the one with the best
aerodynamics, the wings, flares and fat tyres added over the years all adding
to drag. If the smooth roof, introduced
on the LP400 S in 1978, improved aerodynamics, it wasn’t enough to compensate.
The influential but short-lived service
The evolution of the internet since it began to assume its modern form (after the world wide web was “bolted on” in 1991, gaining something like critical mass around 1993) is characterized by a number of separate, parallel and sometimes intersecting threads and probably no application (although technically it was a service) was so emblematic of the trends than Periscope. Periscope was created because someone found the then text-only Twitter (now X) compelling but was annoyed at having to go elsewhere look for video feeds relating to what was being tweeted. The Periscope model was to take advantage of the ubiquity of (1) smartphones meaning high-definition video could, worldwide, be created by billions of users at a moment’s notice and (2) the increasing availability of bandwidth which made real-time streaming practical and what emerged was a system noted for its simplicity; a few taps and whatever one was filming was being streamed.
Send (left) & receive (right): Periscope's simple streaming model.
In the way corporations sometimes do things, Twitter bought Periscope even before the product’s official release and success was immediate, the service quickly among the most popular with support notably coming from legacy broadcasters including the BBC which used the system as a low-cost form of content dissemination; in effect what used to be an “outside broadcast van” (literally a truck packed with cameras and transmission equipment which, with staff and other overheads cost sometimes millions a year to run and could be in one place at a time) was suddenly in the pockets of every staff member. It was also in the pockets of everyone else, some of who were entrepreneurial and before long, Periscope streams of live events (for which broadcasters and others had paid sometimes millions for exclusive rights) and content on screens (cinemas, televisions etc) were being packaged for profit, cannibalizing many pay-per-view (PPV) business models. A flurry of takedown notices (a specialized form of a C&D (cease & desist letter) ensued. Periscope however became a victim of its own success, its model quickly available in many other ways and its functionality was “folded into” Twitter, the service discontinued in March 2021, much of the (not legally challenged) legacy content remaining available on X to this day.






No comments:
Post a Comment