Virus
(pronounced vahy-ruhs)
(1) An sub- or ultra-microscopic (20 to 300 nm diameter),
metabolically inert, non-cellular infectious agent that replicates only within the cells of
living hosts, mainly bacteria, plants, and animals: composed of an RNA or DNA
core, a protein coat, and, in more complex types, a surrounding envelope. Because viruses are unable to replicate
without a host cell, they are not considered living organisms in conventional
taxonomic systems (though often referred to as live (in the sense of active) when
replicating and causing disease.
(2) A quantity of such infectious agents.
(3) In informal use, metonymically, A disease caused by such an infectious agent; a viral illness.
(4) Venom, as produced by a poisonous animal etc (extinct in this context).
(5) Figuratively, any malicious or dangerous entity that spreads from one place or person to another; a corrupting influence on morals or the intellect.
(6) In computing, a segment of often self-replicating code furtively planted in a computer program, either to damage a system or for financial gain by a variety of fraudulent techniques.
(7) In computing (loosely used), any form of malware.
Late 1300s: From the Middle English virus (poisonous substance (this meaning now extinct in this context)), from the Latin vīrus (slime; venom; poisonous liquid; sap of plants; slimy liquid; a potent juice), from rhotacism from the Proto-Italic weisos & wisós (fluidity, slime, poison) probably from the primitive Indo-European root ueis & wisós
(fluidity, slime, poison (though it may originally have meant “to melt away, to
flow”), used of foul or malodorous fluids, but in some languages limited to the specific sense of "poisonous fluid") which was the source also of the Sanskrit
visam (venom, poison) & visah (poisonous), the Avestan vish- (poison), the Latin viscum (sticky substance, birdlime), the
Greek ios (poison) & ixos (mistletoe, birdlime), the Old
Church Slavonic višnja (cherry), the Old
Irish fi (poison) and the Welsh gwy (poison). It was related also to the Old English wāse (marsh). Virus is a noun & a (rare) verb and viral is an adjective; the noun plural is
viruses.
The original meaning, "poisonous substance”,
emerged in the late fourteenth century and was an inheritance from the Latin virus (poison, sap of plants, slimy
liquid, a potent juice) from the Proto-Italic weis-o-(s-) (poison), probably
from the primitive Indo-European root ueis-,
thought originally to mean "to melt away, to flow" and used of foul
or malodorous fluids, but with specialization in some languages to mean
"poisonous fluid". It’s the
source of the Sanskrit visam (venom,
poison) & visah (poisonous), the Avestan
vish- (poison), the Latin viscum (sticky substance; birdlime) the
Greek ios (poison) & ixos (mistletoe, birdlime), the Old
Church Slavonic višnja (cherry). The Old
Irish fi (poison) and the Welsh gwy (poison). The meaning "agent that causes
infectious disease" emerged in the 1790s, the medical literature of the time describing their manifestation in especially disgusting terms (the word pus most frequent) and one dictionary entry of 1770 contains the memorable: "a kind of watery stinking matter, which issues out of ulcers, being endued with eating and malignant qualities". As early as 1728 (borrowing from the earlier sense of "poison"), it had been used in reference to venereal
disease, the first recognizably modern scientific use dating from the 1880s. The first known citation in the context of
computing was by Gregory Benford (b 1941) who published The Scarred Man (1970) although it’s often credited to David
Gerrold (b 1944), who used the word in this context in When HARLIE
Was One (1972).
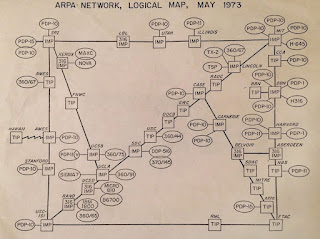
Before the internet: ARPANET network schematic 1973.
In
computing, theoretical work on the self-replicating code (which is the core of
a digital virus) was published as early as 1971 and what’s regarded as the first
object to behave like a virus (though technically, it would now be called a worm) was released as a harmless amusement on ARPANET
(Advanced Research Projects Agency Network) (ARPANET), the internet’s precursor
network. It was called “creeper, catch
me if you can!" and, perhaps predictably, other nerds rose to the challenge
and release the “reaper” their own worm which killed whatever creepers it found. Creeper & reaper conducted their cat
& mouse game on Digital Equipment Corporation's (DEC) PDP-10, predecessor
to the famous PDP-11 mini-computer and at this point, viruses were genuinely harmless (if time wasting) activities conducted between consenting nerds in the privacy of their parochial networks. However, it was the development of the personal computer (PC) from 1975 and especially the subsequent adoption by business of the IBM-PC-1 (1981) and its clones which created the population in which viruses could spread and while relatively harmless creations like Stoned (1987) tended to amuse because they did little more that display on the screen of an infected device the message "Your PC is now Stoned", there were many others which were quite destructive. The first which came to wide public attention was probably Melissa (1999) which caused much economic loss and the discussion of which (by mostly male writers in the specialist press) excited some criticism from feminists who objected to headlines like "Melissa was really loose, and boy did she get around".

The late John McAfee (1945–2021) who led an interesting and varied life.
In medicine, the first antivirus was available in 1903, an equivalent (shrink-wrap)
product for computers apparently first offered for sale in 1987 although there
seems no agreement of which of three authors (Paul Mace, Andreas Lüning &
the late John McAfee) reached the market first.
The adjective viral (of the nature of, or caused by, a virus) dates from
1944 as applied in medicine whereas the now equally familiar, post
world-wide-web sense of stuff "become suddenly popular through internet
sharing" is attested by 1999 although most seem convinced it must have
been in use prior to this.
The rhinovirus (one of a group of viruses that
includes those which cause many common colds) was first described in 1961, the
construct being rhino- (from the Ancient Greek rhino (a combining form of rhis (nose) of uncertain origin) + virus. The noun virology appeared in 1935 to describe
the then novel branch of science and parvovirus (a very small virus), the
construct being parvi- (small, little)
+ the connecting element -o- + virus was coined in 1965 to describe the decreasingly
small objects becoming visible as optical technology improved. The rotavirus (a wheel-shaped virus causing
inflammation of the lining of the intestines), the construct being rota (wheel)
+ virus dates from 1974.
Diagram of a retrovirus.
The adjective virulent dates from circa 1400 in
reference to wounds, ulcers etc (full of corrupt or poisonous matter), from the
Latin virulentus (poisonous), from virus;
the figurative sense of "violent, spiteful" attested from circa
1600; virulently the related form. The
mysterious reovirus was a noun coined
in 1959 by Polish-American medical researcher Dr Albert Sabin (1906-1993), the “reo-“ and acronym for “respiratory
enteric orphan”, to describe viruses considered orphans in the sense of not being
connected to any of the diseases with which they were associated. More technical still was the (1977) retrovirus,
an evolution of the (1974) retravirus (from re(verse) tra(nscriptase) +
connective -o- + virus), explained by it containing reverse transcriptase, an
enzyme which uses RNA instead of DNA to encode genetic information, thus reversing
the usual pattern. While these things are
usually the work of committees, there seems to be nothing in the public record to
suggest why “retro-“ was preferred to “retra-“, the assumption being “retro-“
more explicitly indicated "backwards."
The condition was first isolated in Tanzania in 1952, the word Chikungunya from the Kimakonde language which translates literally as "to become contorted" although the World Health Organization (WHO) lists the common symptoms as a persistent headache, swollen joints, muscle pain and a rash which typically appears first on the extremities.

In 2014, while on holiday in French Polynesia, Lindsay Lohan was infected with Chikungunya, a virus (CHIKV) spread by the bites of infected (usually the Aedes) mosquitoes; it causes severe joint pain, headache, fever, nausea, fatigue and rash and flu-like symptoms but can occasionally be fatal. The word Chikungunya from the Kimakonde language and translates literally as "to become contorted"; the condition was first isolated in Tanzania in 1952 before spreading around the Indian Ocean region, south-east Asia and the Pacific islands, cases emerging for the first time in the Caribbean in 2013 while until recently, it was rare in the US and Europe, most victims having traveled from affected areas. There is no cure or vaccine, and the illness can last from several days to as long as a few weeks. Ms Lohan advised those in susceptible regions to use bug spray and posted on Instagram a photo from the beach, captioned "I refuse to let a virus effect (sic) my peaceful vacation."
In August 2025, wire services began reporting Sri Lanka was facing its worst Chikungunya outbreak in two decades, public health experts linking the spread (the virus since earlier in the year widespread in southern China) to climate change, mosquito habitats spreading as weather patterns shift. In Beijing, despite Chikungunya not being spread by human-to-human contact, the ruling CCP (Chinese Communist Party) ordered mass quarantines with the southern province of Guangdong thought worst afflicted. With the CCP having perfected the protocols established during the Covid-19 pandemic, infected residents were confined to “quarantine wards” in hospitals and placed in beds covered by mosquito nets; unless testing negative, there they must remain for seven days. The CCP is applying technology to the problem, swarms of drones being deployed spraying insecticide, the missions said to be both “targeted” (ie the drone’s sensors being used by an on-board AI (artificial intelligence) engine to detect possible mosquito breeding areas) and “carpeting” (ie soaking a defined area in a way analogous to the “carpet bombing” (also as “area bombing”) of cities which was one of the more controversial strategies of World War II (1939-1945).
Biological warfare is also being pursued: (1) millions of non-transmissive “elephant mosquitoes” being released, their larvae devouring the smaller, virus-carrying pests and (2) thousands of mosquito-eating fish being placed in public ponds. Once the Aedes mosquito becomes endemic to an area, it’s reproduction can be difficult to restrict, one Chinese public health specialist confirming breeding was possible in as small a quantity of liquid as that which might accumulate in an upturned bottle cap. In Guangdong, representatives of the CCP vowed to take “decisive and forceful measures” with residents ordered to remove stagnant water (threats of fines up to US$1,400 a nudge towards compliance). As well as a north-south thing, climate change is also an east-west phenomenon and disease transmission vectors can travel with weather patterns, the ECDC (European Center for Disease Prevention and Control) in July reporting some quarter-million cases with 90 confirmed deaths. The US CDC in August issued a Level 2 travel notice (practice enhanced precautions) for those going to China, two notches down for Leve 4 (avoid all travel to the region).
Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) assembly and egress.
Not alive in the technical sense defined in
biology, a virus is a biological agent which reproduces inside the cells of
living hosts. When infected by a virus,
a host cell is forced quickly to produce thousands of identical copies of the
original; unlike actual living things, viruses do not have cells that divide,
new viruses being assembled in the infected host cell. Unlike simpler infectious agents, viruses
contain genes so they mutate and evolve and thousands are known to exist. Viruses are tiny, much smaller than bacteria
and it can require more than a million of them, side by side, to reach one inch
(25 mm) and although a theory of viruses was constructed after French and
Russian experiments in the 1880s, it wasn’t until the electron microscope became
available in 1931 that the first images were captured. Where there is life, there are viruses and it’s
thought likely they have existed either since, or very shortly after, the first
living cells evolved; it’s not impossible the first cellular forms would now, technically,
be classified as viruses. Viruses can be
benign and bacteriophages are viruses that infect bacteria, used in eastern
Europe since the nineteenth century to treat infection but almost ignored since
the development of antibiotics. With the
growth in antibiotic resistance, there’s now renewed interest. Viruses also perform a useful role in
ecology, killing around a fifth of oceanic biomass, the increased respiration
in the seas ultimately reducing the atmospheric carbon dioxide by some three gigatons
per year.
During the initial 2019 outbreak in Wuhan of what
is now called COVID-19, both virus and disease were mostly referred to as
"coronavirus", "Wuhan coronavirus" or "Wuhan
pneumonia". There had been a long
tradition of naming diseases after the geographical location where they were
first reported (Hong Kong flu, Spanish flu etc) but this could be misleading. The Spanish flu, associated with the pandemic
of 1918-1920, was actually first detected elsewhere, either on the World War I battlefields
of France or (more probably) a military camp in the United States but, because Spain was a
neutral in the conflict, there was no military censorship to limit reporting so
warnings about this especially virulent influenza were printed in the Spanish
press. From here, it was eventually
picked up and publicized as “Spanish flu” although, doctors there, in an early
example of contract tracing, were aware of vectors of transmission and insisted
it was the “French flu” because this was where their back-tracing led. This had no
effect beyond Spain and it’s ever since been known as “Spanish flu” although the practice of using geographical references has now been abandoned, a linguistic sanitization which has extended to anything likely to cause offence, the recently topical Monkeypox now called Mpox which seems hardly imaginative.

In January 2020, the World Health Organization’s
(WHO) International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) recommended the
name 2019-nCoV & 2019-nCoV acute respiratory disease as interim names for virus
and disease respectively (although “human coronavirus 2019”, “HCoV-19” & “hCoV-19”
also exist in the record). The committee’s
recommendation conformed to the conventions adopted after it was decided in
2015, to avoid social stigma, to cease the use of geographical locations or identities
associated with specific people(s) in disease-related names. Although well understood by scientists, the
WHO must have thought them a bit much for general use and in February 2020,
issued SARS-CoV-2 & COVID-19 as the official nomenclature: CO=corona, VI=virus,
D=disease & 19=2019 although for a while, confusingly, documents issued by
the WHO sometimes referenced “COVID-19 virus” rather than the correct
SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; the name adopted
because of the close genetic relationship to the first SARS outbreak in 2003
(now retrospectively listed as SARS-Cov-1).
One of
civilizations modern quests is the hunt for the “viral video” (video content
posted to the internet which rapidly and at scale is passed from user to user
in a pattern analogous to the spread of a virus). A viral video can bring one (at least a
transitory fifteen minutes) fame, cash and perhaps a spike in the traffic to
one’s OnlyFans page but, depending on the content and context, what can also
ensue is infamy, cancellation or incarceration so, as the Justine Sacco (b 1985) “incident” illustrates, caution should be a prelude to posting. A minor industry has sprung up to advise all
who aspire to be content providers and one popular theme is what makes a clip
go viral. On the basis of posted advice,
it seems clear there’s no one set of parameters which need be used but there’s
certainly a collections of characteristics which encourage sharing and while virality
remains unpredictable, most clips which spike do share common traits although
with some obvious exceptions, the phenomenon tends to be siloed, a clip which
wildly goes vial among one market segment can be almost un-shared within
another. The markers likely to trigger a
viral reaction have been categorized thus:
(1) Original
content: This need not of necessity be something novel or in any way unique but
both those qualities can be valuable, something genuinely new most likely to grab
attention.
(2) Creativity:
This can mean something unconventional in approach or the use of existing techniques
with high production values.
(3) Emotional
Resonance: Known also as “emotional
manipulation”, content which can evoke feelings of joy, awe surprise, sadness, rage,
disgust etc are more likely to be shared.
(4)
Brevity: Most viral are videos which are short (less than two minutes is
typical) and to some extent this is technologically deterministic, so much
viral media coming from sites which curate such material and this has
encouraged a ecosystem of what are now called “viral sites” (BuzzFeed,
Upworthy, Distractify, LittleThings, Thought Catalog, UPROXX, Vox, Daily Dot,
Ranker, Words etc). Students of cause
& effect can ponder the interplay between the emergence of these platforms and
the alleged shortening of the planet’s collective attention span.
(5) The hook:
Two minutes is a long time in the context of scrolling and while it’s not
impossible for a clip where the “best big” comes at the end to go viral, it is
less likely because not enough viewers will have persisted for it to gain
critical mass (hence the oft-seen plaintive plea "watch to the end!"). Ideally, interest to the
point of being committed to watch to the end should be captured in the first
few seconds. If the material is in the
form of music, it should appeal (in a TikTok sort of way) with the sort of
formula the pop music generators perfected in decades past.
(6) Entertaining:
Clips go viral for all sorts of reasons but nothing seems to work better that
something which makes people laugh; it’s more popular even than outrage, the
internet’s other way of life.
(7) Relatability:
Relatability (that with which people can identify) is a concept which can be vertical
(something with great appeal to certain section of the population) or
horizontal (something with general appeal to many sections of the population). Content with a universal appeal (cross-cultural
relevance) should in theory produce the greatest numbers but something aimed
specifically at one market can produce greater tangible results (revenue).
(8) A
twist: The ultimate viral video content is probably something with a hook at
the start which grabs the attention, maintains a commitment to watching and
then concludes with a dramatic, unexpected or funny ending.
(9) Ease of
sharing: When file formats were not (more or less) standardized and
cross-platform compatibility couldn’t be assumed, this was something to consider
but now most content is optimized for the majors (TikTok, Instagram, YouTube etc), the process close to effortless.
(10) A Call-to-Action:
This means something which encourages sharing and that can be explicit (“please share”) or a subliminal message
which induces in viewers either a desire to share or a feeling they are somehow
obliged to share. Those which are controversial
(the more polarizing the better) and which enable users to engage in “virtue
signalling” (sharing a clip as a display of moral superiority) should produce
more reaction.
(11) Relevance:
If it’s funny enough nothing else really matters but something tied to the
zeitgeist tends most quickly to gain traction.
These can be tied to trending hashtags or challenges on social media and
are the most obvious form of encouraging interaction without demanding any real
commitment.
(12) Celebrity
association. This need not be an endorsement
(there evidence there’s now much cynicism about this) but if a celebrity shares
something, it should be an accelerant in the process.
A classic viral clip: Man in Finance mixed by DJs Billen Ted & David Guetta, written and sung by Megan Boni (Girl on Couch).
I'm looking for a man
in finance
Trust fund
Six-five (ie 6 foot,
five inches tall)
Blue eyes
That's all I want
The lyrics
to the track Man in Finance (sometimes
as Looking for a Man in Finance) were
written by Megan Boni (b 1997 and now better known as @girl_on_couch). In April 2024 Ms Boni uploaded the clip (as a
cappella piece) to TikTok and she says it was a parody of the unrealistic
expectations of men held by young single women such as herself. Attached to the original (a viral-friendly 19
seconds in duration) upload, Ms Boni requested DJs in her audience to “…make this into
an actual song plz just for funzies.” The DJs responded, the edited clip went viral
and Ms Boni quit her “9 to 5” to enter the music industry.
Still looking: The admirable Megan "Girl on Couch" Boni, perched on couch.
Catchy though it was, dropping the tune was not without risk because the internet is riddled with those combing sites to find some way of being offended (or disrespected, marginalized
etc) and in an interview with the BBC (British Broadcasting Corporation) she did note one comment on her post was
that wanting a man with “blue eyes”
meant she must be “racist” but there was little support for that
and she escaped cancellation. Still, the
risks were clearly there because each line was laden with offence for the hordes anxious to be outraged:
I'm looking for a man
in finance
(critique: supports a system which is exploitative and exists to alienate to people from the fruits of their labor by appropriating the surplus value).
Trust fund (critique: materialist)
Six-five (critique: heightist and thus exclusionary)
Blue eyes (critique: racist and thus
exclusionary)
That's all I want (there will be those who think this objectionable)
Really,
people should just enjoy the beat. As a
parody it works well, a young spinster lamenting her status as a singleton by
restricting the acceptable catchment of who might seek courtship to (1) “a man”
(thereby excluding half the population), (2) employed in the “finance”
industry (a tiny fraction of the male population), (3) the beneficiary of a “trust fund”
(a tiny fraction of men working in the finance industry) (4) “six-five”
tall (a tiny fraction of men working in the finance industry who are the beneficiaries
of a trust fund) and (5) has “blue eyes” (an unknown but small percentage of 6’
5" (1.95 m) tall men who are the beneficiaries of a trust fund and employed in the
finance industry). That math is of
course what makes the last line (That’s all I want) so funny. Ms Boni should maintain her high standards because
she deserves to find the man of her dreams.








%20assembly%20and%20egress.jpg)





